
For EDT 645 we examined our own computers operating system and installed software. The information below is what I found on my computer. Operating System- Windows XP Home When I purchased my current laptop Windows XP Home was pre-installed. I would have preferred Windows XP Professional, but that option was not available with an “off the shelf” system which meant my requirements and timeframe for purchasing a computer. The differences between Windows XP Home and Professional are noted: http://www.microsoft.com/windowsxp/pro/howtobuy/choosing2.mspx . I found Windows XP to be a great operating system with only a few features I preferred with earlier versions of Windows (Windows ME, Windows 98 and Windows 95). Some inconveniences I noticed with Windows XP are many options are now “hidden” that were easily accessible in previous versions. Windows XP uses more memory and hard disk space. Windows XP descended from Windows NT whereas Windows 1.0-3.11, Windows 9x and Windows ME descended from DOS. Microsoft provides a nice checklist ofWindows feature comparisons that includes: Windows 9x, Windows ME and Windows XP Home: (http://www.microsoft.com/windowsxp/home/evaluation/whyupgrade/featurecomp.mspx) The benefits are numerous the top ten reasons to upgrade are: http://www.microsoft.com/windowsxp/home/evaluation/whyupgrade/top10.mspx
Overall, Windows XP Home is a user-friendly operating system. System Requirements- Minimums :
If you use your computer for more than just a couple of hours per week, you really will not find the Microsoft minimums acceptable, and should use the Ludens-adjusted minimums. (http://windows.about.com/library/weekly/aa011007a.htm) Other minimum requirements may be necessary to run certain features of Windows XP Home. Applying the official Ludens Reality Adjustment, ™ however, yields the following minimums:
Software Specifications: After running the Belarc Advisor, a program that provides a computer profile summary including all software installed on a system, I realized I am an operating systems worst nightmare. My computer profile summary resulted in seven pages and listed over 200 programs I have installed on my computer. I did notice programs I have installed were not listed (Netscape, Apache Ant, Apache Tomcat) and the second partition running Red Hat Enterprise WS was not included. A condensed list of programs and specifications on my computer:
Other Operating Systems (older versions): Windows History: abridged (http://www.microsoft.com/windows/WinHistoryDesktop.mspx) Many longtime PC users trace the Microsoft Windows® operating system to the 1990 release of Windows 3.0, the first widely popular version of Windows and the first version of Windows many PC users ever tried. However, Microsoft initially announced the Windows product seven years earlier and released the first version in 1985. 1985: Windows 1.0- 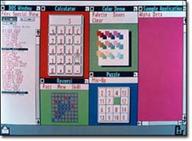 1987: Windows 2.0- Windows 2.0 took advantage of the improved processing speed of the Intel 286 processor, expanded memory, and inter-application communication capabilities made possible through Dynamic Data Exchange (DDE). With improved graphics support, users could now overlap windows, control screen layout, and use keyboard combinations to move rapidly through Windows operations. Many developers wrote their first Windows–based applications for this release. The follow-up release, Windows 2.03, took advantage of the protected mode and extended memory capabilities of the Intel 386 processor. 1987: Windows 2.0- Windows 2.0 took advantage of the improved processing speed of the Intel 286 processor, expanded memory, and inter-application communication capabilities made possible through Dynamic Data Exchange (DDE). With improved graphics support, users could now overlap windows, control screen layout, and use keyboard combinations to move rapidly through Windows operations. Many developers wrote their first Windows–based applications for this release. The follow-up release, Windows 2.03, took advantage of the protected mode and extended memory capabilities of the Intel 386 processor.
1990: Windows 3.0- The third major release of the Windows platform from Microsoft offered improved performance, advanced graphics with 16 colors, and full support of the more powerful Intel 386 processor. A new wave of 386 PCs helped drive the popularity of Windows 3.0, which offered a wide range 1993: Windows for Workgroups 3.11 -A superset of Windows 3.1, Windows for Workgroups 3.11 added peer-to-peer workgroup and domain networking support. For the first time, Windows–based PCs were network-aware and became an integral part of the emerging client/server computing evolution. Windows for Workgroups was used in local area networks (LANs) and on standalone PCs and laptop computers. It added features of special interest to corporate users, such as centralized configuration and security, significantly improved support for Novell NetWare networks, and remote access service (RAS).
1993: Windows NT Workstation 3.5- The Windows NT Workstation 3.5 release provided the highest degree of protection yet for critical business applications and data. The product also offered 32-bit performance improvements and better application support, including support for NetWare file and print servers. Other improved productivity features included the capability to use friendlier, long file names of up to 255 characters. 1995: Windows 95- Windows 95 was the successor to the three existing general-purpose desktop operating systems from Microsoft—Windows 3.1, Windows for Workgroups, and MS-DOS. Windows 95 integrated a 32-bit TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) stack for built-in Internet support, dial-up networking, and new Plug and Play capabilities that made it easy for users to install hardware and software. 1996: Windows NT Workstation 4.0- This upgrade to the Microsoft business desktop operating system brought increased ease of use and simplified management, higher network throughput, and tools for developing and managing intranets. Windows NT Workstation 4.0 included the popular Windows 95 user interface yet provided improved networking support for easier and more secure access to the Internet and corporate intranets. In October 1998 , Microsoft announced that Windows NT would no longer carry the initials NT and that the next major version of the business operating system would be called Windows 2000.1998: Windows 98- Windows 98 was the upgrade from Windows 95. Described as an operating system that "Works Better, Plays Better," Windows 98 was the first version of Windows designed specifically for consumers. With Windows 98, users could find information more easily on their PCs as well as the Internet. Other ease-of-use improvements included the ability to open and close applications more quickly, support for reading DVD discs, and support for universal serial bus (USB) devices. 1999: Windows 98 Second Edition -Windows 98 SE, as it was often abbreviated, was an incremental update to Windows 98. It offered consumers a variety of new and enhanced hardware compatibility and Internet-related features. Windows 98 SE helped improve users' online experience with the Internet Explorer 5.0 browser technology and Microsoft Windows NetMeeting® 3.0 conferencing software. It also included Microsoft DirectX® API 6.1, which provided improve support for Windows multimedia, and offered home networking capabilities through Internet connection sharing (ICS). Windows 98 SE was also the first consumer operating system from Microsoft capable of using device drivers that also worked with the Windows NT business operating system. 2000: Windows Millennium Edition (Windows Me)- Designed for home computer users, Windows Me offered consumers numerous music, video, and home networking enhancements and reliability improvements.Windows Me was the last Microsoft operating system to be based on the Windows 95 code base. Microsoft announced that all future operating system products would be based on the Windows NT and Windows 2000 kernel.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Acronym |
Term |
Description |
Analog |
describes a device or system that represents changing values as continuously variable physical quantities. A typical analog device is a clock in which the hands move continuously around the face. |
|
Antivirus Program |
A utility that searches the hard disk for viruses and removes any that are found. Most antivirus programs include an auto-update feature so that it can check for new viruses as soon as they are discovered. |
|
Acronym |
Term |
Description |
Application software |
applications software sits on top of systems software because it is unable to run without the operating system and system utilities. Also called end-user programs includes database programs, word processors, and spreadsheets. |
|
GUI |
Graphical User Interface |
Provides visual cues such as icons to help the user access other programs on the computer. GUI's are used instead of using command languages - text based commands. Microsoft Windows is and example of a popular GUI. |
ICS |
Internet Connecting Sharing |
a method for connecting multiple computers in a LAN to the Internet through a single connection and a single IP address. Sharing an Internet connection can be achieved through either software or hardware solutions. |
MHz |
Megahertz |
One MHz represents one million cycles per second. The speed of microprocessors, called the clock speed, is measured in megahertz. For example, a microprocessor that runs at 200 MHz executes 200 million cycles per second. |
Multitasking |
The ability to execute more than one task at the same time, a task being a program. One CPU, switches from one program to another so quickly that it gives the appearance of executing all of the programs at the same time. |
|
Network |
A group of two or more computer systems linked together. There are many types of omputer networks, including: WANs, LANs, CANs, MANs, HANs. Connecting two or more computers together with the ability to communicate with each other. |
|
OS |
Operating System |
The most important program that runs on a computer, must have to run other programs. Recognizes input from keyboard, mouse, sends output to the display screen, keeps track of files and directories on the disk, and controlling peripheral devices. |
SVGA |
Super Video Graphics Array |
a graphics display system for PCs developed by IBM. VGA has become the de facto standards for PCs. VGA uses analog signals rather than digital signals. The SVGA standards are developed by a consortium of monitor and graphics manufacturers called VESA. |
Sysedit |
Utility that enables a user to edit important files such as the sytem.ini, win.ini, autoexec.bat and config.sys. Included in earlier versions of Windows. Changed to msconfig in Windows 98. |
|
sysadmin |
System Administrator |
An individual responsible for maintaining a multi-user computer system, including a local-area network (LAN). Typical duties include: adding and configuring new workstations, setting up user accounts, installing system-wide software, etc… |
System software |
Refers to the operating system and all utility programs that manage computer resources at a low level. Systems software includes compilers, loaders, linkers, and debuggers. |
|
Virus |
A program or piece of code that is loaded onto your computer without your knowledge and runs against your wishes. Viruses can also replicate themselves. All computer viruses are manmade and can be very damaging to computers and networks. |
|
Acronym |
Term |
Description |
Wizard |
A utility within an application that helps you use the application to perform a particular task. For example, a "letter wizard" within a word processing application would lead you through the steps of producing different types of correspondence. |
|
Worms |
A worm is a special type of virus that can replicate it self and use memory, but cannot attach itself to other programs. |
Resources:
About.com http://windows.about.com/library/weekly/aa011007a.htm
Belarc Advisor Program http://www.belarc.com/free_download.html
Computer Hope http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/
Microsoft http://www.microsoft.com
Webopedia http://www.webopedia.com
Educational Technology encompasses many areas which are included in this website. If you did not find the information you were looking for on this page, please visit other topics.
Assessment/Evaluation | Certification Resources | Copyright/Plagiris | Distance Education | Employment | Glossary | Hardware | Instructional Design | Miscellaneous | Research Methods | Sample Documents | Software Applications | Staff Development | Technology Resources | Web Development | Contact
 The first version of Windows provided a new software environment for developing and running applications that use bitmap displays and mouse pointing devices. (Graphical Interface-GUI) Before Windows, PC users relied on the MS-DOS® method of typing commands at the C prompt (C:\). Window users could switch among several concurrently running applications. The product included a set of desktop applications, including the MS-DOS file management program, a calendar, card file, notepad, calculator, clock, and telecommunications programs, which helped users manage day-to-day activities.
The first version of Windows provided a new software environment for developing and running applications that use bitmap displays and mouse pointing devices. (Graphical Interface-GUI) Before Windows, PC users relied on the MS-DOS® method of typing commands at the C prompt (C:\). Window users could switch among several concurrently running applications. The product included a set of desktop applications, including the MS-DOS file management program, a calendar, card file, notepad, calculator, clock, and telecommunications programs, which helped users manage day-to-day activities. 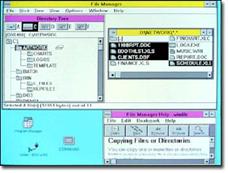 of useful features and capabilities, including: Program Manager, File Manager, and Print Manager. A completely rewritten application development environment and an improved set of Windows icons. The popularity of Windows 3.0 grew with the release of a new Windows software development kit (SDK), which helped software developers focus more on writing applications and less on writing device drivers. Widespread acceptance among third-party hardware and software developers helped fuel the success of Windows 3.0.
of useful features and capabilities, including: Program Manager, File Manager, and Print Manager. A completely rewritten application development environment and an improved set of Windows icons. The popularity of Windows 3.0 grew with the release of a new Windows software development kit (SDK), which helped software developers focus more on writing applications and less on writing device drivers. Widespread acceptance among third-party hardware and software developers helped fuel the success of Windows 3.0. 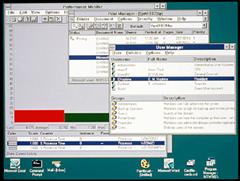

 users can work smarter and faster, thanks to new technical-support technology, a fresh user interface, and many other improvements that make it easier to use for a wide range of tasks.
users can work smarter and faster, thanks to new technical-support technology, a fresh user interface, and many other improvements that make it easier to use for a wide range of tasks.  2002: Windows XP Media Center Edition -For home computing and entertainment, Microsoft released the Windows XP Media Center Edition operating system in October 2002 for specialized media center PCs. With all the benefits of Windows XP Professional, Media Center Edition adds fun digital media and entertainment options, enabling home users to browse the Internet, watch live television, communicate with friends and family, enjoy digital music and video collections, watch DVDs, and work from home.
2002: Windows XP Media Center Edition -For home computing and entertainment, Microsoft released the Windows XP Media Center Edition operating system in October 2002 for specialized media center PCs. With all the benefits of Windows XP Professional, Media Center Edition adds fun digital media and entertainment options, enabling home users to browse the Internet, watch live television, communicate with friends and family, enjoy digital music and video collections, watch DVDs, and work from home. 